Every time something goes wrong somewhere in some blood test or the other for my mom and I feel guilty :(
Last time wen she met her gynae she explained that she is having some ichiness all over the body and then advised the SGPT/SGOT test for mom and they came back high..
Now what might be the reasons for that?
There are several theories as explained by practitioners for this..
Changes in metabolism during pregnancy, weight gain can cause elevated liver tests that should return to normal as your body returns to pre-pregnancy state. One should exclude viral hepatitis with the appropriate blood tests. You should continue with follow-up liver tests until normal values are obtained.
There are many conditions that are commonly associated with elevations of the Liver Function Tests SGOT/AST and SGPT/ALT. There are numerous causes of having an elevation of these enzymes. SGPT/SGOT are enzymes that are associated with the function of your liver and the conversion of glucose and are usually found in the mitochondria of the liver cells. Different levels of these enzymes can indicate differing conditions and causes. These may include gallbladder disease, hepatitis, fatty liver, cirrhosis, infectious mononucleosis, alcoholism, medications and drug toxicity, CHF, heart attack, heart muscle damage, skeletal muscle injury, renal infarct, certain types of anaemia, malignancy and others. Further tests will very likely be ordered to ascertain the cause of your sister’s elevated levels. Without access to the full LFT report, there are no further details to work on or discuss.
ALT (SGPT) and AST (SGOT) are enzymes made in the liver. They are also known as transaminases. The liver uses these enzymes to metabolize amino acids and to make proteins. When liver cells are damaged or dying, ALT and AST leak into the bloodstream. Many different things can cause liver enzymes to rise above normal levels: Viral hepatitis Excessive alcohol intake/Alcoholic liver disease Liver inflammation from medications such as overdose of Acetaminophen ( Tylenol) and certain herbs, Auto-immune hepatitis - a condition where a person's immune system mistakes the liver for an invader and attacks it, Fatty liver- fat build -up in liver cells, called steatohepatitis when the fatty liver is inflammed - NASH Inherited liver diseases Liver tumors Heart failure Inflammation in the liver or gallbladder Gallstones
To help with constipation and other IBS (Irritable Bowel Syndrome) symptoms during pregnancy, some women take medications. Not all medications that may be used to treat irritable bowel syndrome are safe for pregnancy. Therefore, you should discuss medical treatment with your doctor before taking any drug. However, the following is a list of medications that are usually safe to take during pregnancy:
o Acetaminophen (IE Tylenol) - helps with pain and discomfort
o Bentyl/Dicyclomine - prevents muscles spasms in the stomach and bladder and helps to relax them. It also reduces the production of stomach acid.
o Diclectin - helps with morning sickness
o Simethicone - helps to alleviate gas in the intestinal tract.
Medications are not the only answer when it comes to helping pregnant women treat their IBS symptoms. Alternative treatments include:
o Drinking plenty of water - prevents dehydration and helps with digestion
o Regular and safe pregnancy exercises - helps aid in digestion and reduces stress
o Sufficient sleep - reduces stress
o High fiber diet - Helps move slow bowels. This includes foods such as fruit, vegetables, and high fiber cereals. Note: keep in mind that if your IBS symptoms occur because of certain fiber foods, don't include these as apart of your diet.
o Soluble fiber supplements - may help with diarrhea and constipation
o Ginger tea - Ginger tea can help treat morning sickness
o Hypnosis - This psychological treatment can be used to individually treat the symptoms a woman is experiencing.
As you can see, there are plenty of ways a pregnant woman can deal with IBS. The trick is to know what treatments work best, and incorporate them into a healthy and active lifestyle.
http://ezinearticles.com/Obstetric Cholestasis or Intrahepatic Cholestasis of Pregnancy (ICP)
What is ICP?
ICP is defined as a pregnancy-related liver condition that affects the flow of bile (a liver-produced substance that aids in the digestion and absorption of fats) to a woman’s body. This condition results in a build-up of bile acids in the blood, which in turn can lead to severe itching, and in more rare cases, jaundice.
The onset of ICP during pregnancy usually begins during the third trimester – as this is when hormone concentrations are highest – although some reports indicate it can begin as early as the first few weeks of pregnancy.
Unfortunately, the exact cause of ICP has not been determined. However, there does appear to be a genetic component to this disease; about half of all women with ICP reported having liver-related disorders in the family.
What are Intrahepatic Cholestasis of Pregnancy Symptoms?
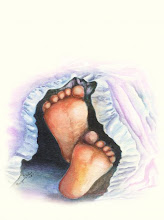
The primary symptom of ICP is severe itching. The itching generally progresses in severity, and may develop to the point that it interferes with a woman’s daily activities, including sleep. Although the itching sensation can be present on any part of the woman’s body, it is most commonly felt on the palms of the hands or the soles of the feet.
In addition, women may experience yellowing of their skin or whites of the eyes – also known as jaundice. This is estimated to occur in about 20% of women with ICP.
How is ICP Treated?
In previous years, the primary form of medicinal treatment for ICP was a cholesterol-lowering drug called cholestyramine. However, this drug has recently been proven to be largely ineffective in lowering bile acids. In addition, a number of potentially dangerous side-effects (including vitamin K deficiency) have caused doctors to revoke this form of ICP treatment. Currently, there are several components that generally comprise treatment for ICP:
- Ursodeoxycholic Acid (Actigall): One of the most important treatments for ICP, ursodeoxycholic acid works to improve liver function by replacing toxic bile acids in the bloodstream. It has also been shown to reduce the risk of stillbirth.
- Vitamin K: Although not an essential part of ICP treatment, vitamin K therapy is sometimes recommended to combat the reduced absorption of fat-soluble vitamins that often results from having ICP. Vitamin K deficiencies are associated with increased risk for hemorrhaging in the mother and child.
- Steroids: Because pregnant women with ICP run an increased risk of pre-term labor, steroids may be administered before 32 weeks gestation to ensure the baby’s lungs are mature at birth. The drug may also reduce the itching sensation so commonly associated with ICP.
Mother and baby will also be monitored closely during the pregnancy to ensure normal fetal development is taking place. If any abnormalities are detected, early delivery may be suggested. In addition, the doctor may perform an amniocentesis test at 36 weeks gestation in order to ensure the baby’s lungs are mature enough to survive should early delivery be necessary. If this is so, labor may be induced at 36 or 37 weeks to prevent any ICP-related complications at birth.
http://www.pregnancy-info.net/obstetric_cholestasis.htmlHow is ICP diagnosed?Itching is quite often the only symptom a woman notices when she develops ICP. The itching can vary from person to person on palms of hands, arms, legs, soles of feet or all over the body. It is normally more intense at night. Due to the fact that itching is considered a normal part of pregnancy, testing for ICP is often overlooked. This can be a dangerous mistake. Any complaint of itching during pregnancy should be taken seriously and be evaluated.
Two tests should be administered to women who are experiencing pruritus which include the following:
Serum Bile Acid Test (SBA): The serum bile acid test is the most sensitive indicator of ICP. A diagnosis of ICP is often established when bile acid levels are elevated above the normal range. Since labs use differing testing methods, the normal range may fluctuate from lab to lab. The SBA test is a specialized test that should be administered after a period of fasting, as eating certain foods may increase bile production, although some labs do not make this a requirement and it often does not have a large impact on the overall results.
Standard liver enzymes include Alanine Transaminase (ALT), Aspartate Trasaminase (AST), and Alkaline Phosphotase (ALK) and are often referred to as the transaminases.
ALT is the enzyme produced within the cells of the liver. The level of ALT abnormality is increased in conditions where cells of the liver have been inflamed or undergone cell death. As the cells are damaged, the ALT leaks into the bloodstream leading to a rise in the serum levels. Any form of hepatic cell damage can result in an elevation in the ALT. The ALT level may or may not correlate with the degree of cell death or inflammation. ALT is the most sensitive marker for liver cell damage.
AST also reflects damage to the hepatic cell. It is less specific for liver disease. It may be elevated and other conditions such as a heart attack. Although AST is not a specific for liver as the ALT, ratios between ALT and AST are useful to physicians in assessing the etiology of liver enzyme abnormalities.Alkaline Phosphatase (ALK), is another liver enzyme that is evaluated during a routine LFT, but because this value is normally elevated in pregnancy, it's contribution to the diagnosis of ICP is typically disregarded by specialists.
http://www.itchymoms.com/diagnosis.html
1 comment:
Alanine transaminase (ALT) is a transaminase enzyme. It is also called alanine aminotransferase (ALAT) and was formerly called serum glutamate-pyruvate transaminase (SGPT) or serum glutamic-pyruvic transaminase (SGPT). alanine transaminase
Post a Comment